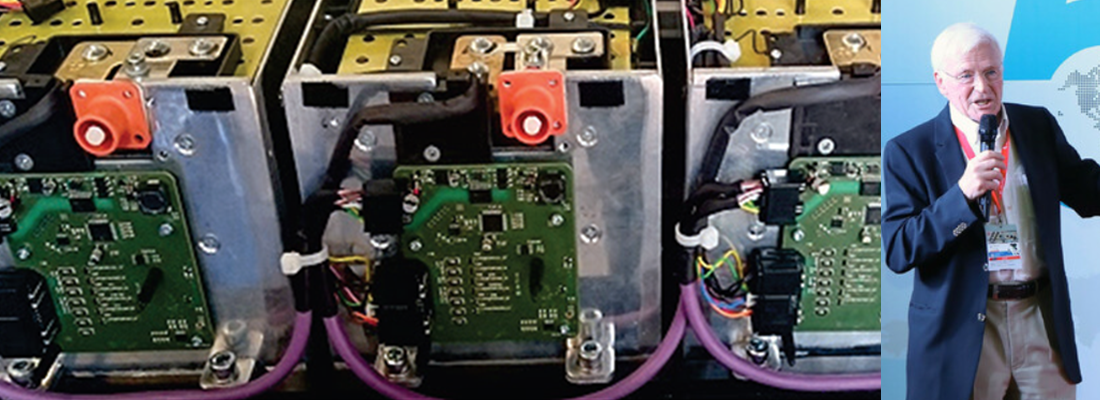
Micro-duty remanufacturing in the automotive field
In this historical moment, where the automotive industry is now also defined by BEVs, e-bikes and e-scooters are becoming increasingly widespread. Consequently, remanufacturing is also evolving to be ready to face a new challenge!
The current scenario of micro-duty in terms of remanufacturing

The current scenario of remanufacturing in the e-bike and e-scooter industry is still in its early stages, but it is gradually gaining attention due to increasing concerns over sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and the growing demand for e-bikes and e-scooters. While remanufacturing processes for traditional bicycles have been established for years, e-bikes and e-scooters face additional challenges, mainly because of their more complex electrical and technological systems. However, there are promising signs of progress, and some companies and initiatives are starting to lay the groundwork for e-bike and e-scooter remanufacturing.
A new approach for remanufacturing
Opening micro - duty to remanufacturing involves designing and building it with remanufacturing in mind, making it easier to repair, refurbish, and reuse components at the end of their life cycle. To achieve this, manufacturers need to adopt specific practices and design principles that facilitate remanufacturing and sustainability.

E-bikes and electric scooters should be designed with easy-to-replace and modular components. The motor, battery, controller, and frame should be separate units that can be easily disassembled and replaced or upgraded. This allows individual parts to be remanufactured without requiring the entire bike to be discarded. Using standard components for motors, batteries, and other parts allows for easier replacement and compatibility across different bike models and generations. Standardization also means that a larger pool of parts can be reused or refurbished, reducing production costs and waste.
Clear documentation is very important. Providing easy-to-understand repair manuals, disassembly guides, and part catalogues can help consumers or repair shops carry out remanufacturing processes effectively. Having access to maintenance and repair instructions is critical for prolonging the life of bikes and scooters.
For remanufacturing, ensuring that the tools required for repairs are readily available and compatible with existing components is essential. If special tools are needed, offering them as part of a service package can encourage repairs and refurbishment over full replacements.
High-Quality Materials
Choosing durable and high-quality materials for key components (such as motors, frames, and wiring) will ensure they can withstand repeated use, refurbishment, and upgrades. For example, using high-quality aluminium alloys for frames or sealed bearings for motors can make them last longer and more suitable for remanufacturing. Components exposed to harsh weather conditions, like the frame, wheels, and battery casing, can be designed with materials or coatings that resist corrosion, further extending their usable life and making them more suitable for remanufacturing.
Battery Design
Designing batteries that can be easily removed, disassembled, and refurbished (replacing cells, repairing wiring, etc.) is essential. Battery packs with easily accessible cells or with replaceable parts can reduce waste and lower the cost of remanufacturing.
E-bikes and electric scooters should be designed in a way that their batteries can be easily recycled at the end of life, and older batteries can be upgraded to newer, more efficient technology (such as replacing older cells with newer, more energy-dense ones).
Wheels, Tires, and Suspension
Rims, spokes, and hubs can be repaired or replaced. Re-lacing and truing the wheels can extend their life. Worn-out tires can be replaced, or tire treads can be repaired if possible.
Forks and rear shocks can be serviced, with seals replaced and the oil replenished to ensure smooth operation.
Software, warranty and Take-Back Programs
As e-bikes and e-scooters often have embedded software to control things like motor performance, battery management, and user interfaces, remanufacturing could involve upgrading or replacing their firmware. This could include optimizing motor assist algorithms, updating their performance settings, or adding new features through software updates.
Allowing consumers to adjust or reprogram settings (e.g., power assist levels, throttle behaviour) could improve their longevity by adapting it to changing needs over time.
Manufacturers can offer take-back or trade-in programs where consumers can return their old e-bikes and e-scooters to the company for refurbishment or recycling. This creates a direct path for remanufacturing while also ensuring that valuable materials are reclaimed.
Offering longer warranties and promoting repair services can encourage consumers to repair and remanufacture their e-bikes and e-scooters instead of discarding them. Extended warranties would also build trust in remanufactured parts, ensuring consumers feel confident in the performance and reliability of refurbished e-bike and e-scooters components.
OEMs and Third-Party Remanufacture
OEMs can collaborate with third-party companies that specialize in remanufacturing e-bike and e-scooter parts, such as batteries and motors. These partnerships would ensure that there is an established infrastructure for remanufacturing that is both efficient and cost-effective.
Creating a network of repair and remanufacturing service centres, possibly authorized by the manufacturer, can ensure that e-bikes and e-scooters are serviced with quality parts and skilled labour. This network would support the entire lifecycle of an e-bike and e-scooter, from initial sale through to remanufacturing and refurbishment.